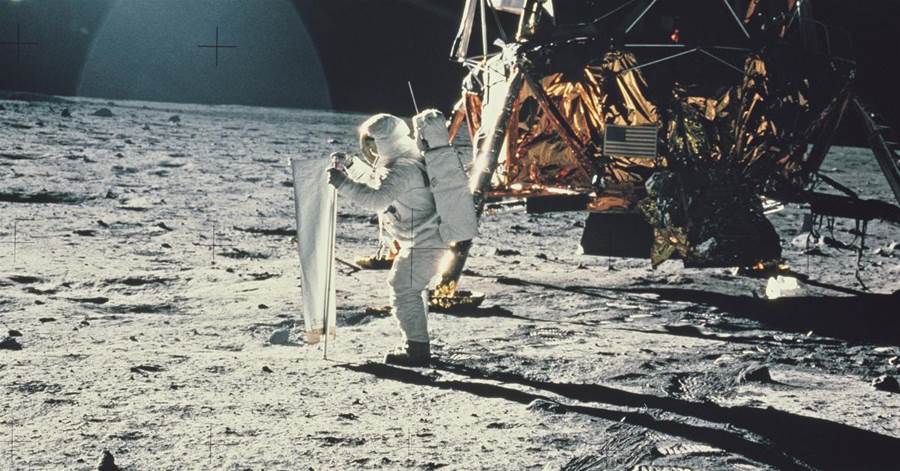
The process of landing on the moon is not as simple as it may seem, and there are several reasons behind it. Despite the advancements made by NASA and other space agencies, landing on the moon continues to pose challenges.
One reason is the sheer distance between Earth and the moon. It takes approximately three days to travel to the moon, and this journey requires carefully calculated trajectories to ensure a successful landing. Any miscalculation can result in a missed landing or even a catastrophic failure.
Another challenge is the moon's surface itself. Unlike Earth, the moon lacks an atmosphere, which means there is no air to slow down a spacecraft during descent.
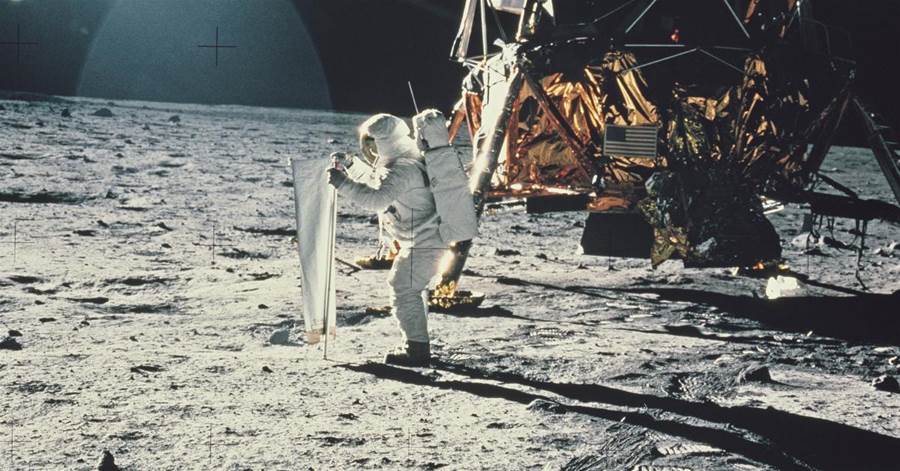
Furthermore, the moon's uneven and crater-ridden surface adds to the complexity of landing. Identifying a smooth and suitable landing site is crucial to minimize the risk of accidents. Additionally, the moon's low gravity poses a unique challenge. While it may seem advantageous, the low gravity makes maneuvering and controlling the spacecraft more difficult.
Despite these challenges, landing on the moon remains a significant goal for space exploration. NASA and other space agencies are continuously working on innovative solutions to overcome these obstacles. The knowledge gained from previous moon landings, such as the Apollo missions, has paved the way for future missions and the eventual establishment of a lunar base. However, it is important to recognize that landing on the moon is a complex endeavor that involves careful planning, precise calculations, and the utilization of advanced technology.








